READ Free Dumps For Microsoft- 70-410
| Question ID 9975 | HOTSPOT
You have three servers named Server1, Server2, and DC1 that run Windows Server 2012 R2. IPv6 addresses and configurations are assigned to all of the servers
by using DHCPv6.
The IPv6 routing on Server1 is shown in the following table.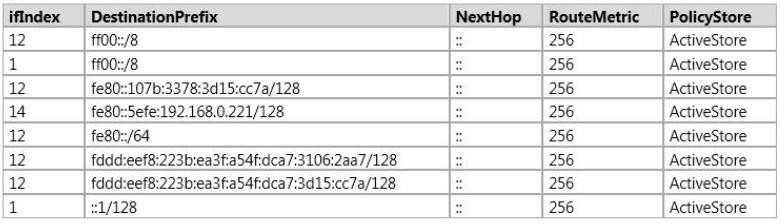
You verify that Server2 can ping the IPv6 address of DC1.
You need to ensure that Server1 can ping the IPv6 address of DC1.
What command should you run on Server1? (To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area.)
Hot Area:
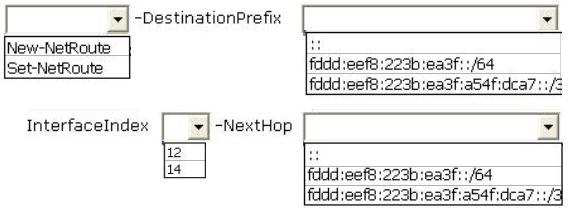
|
| Option A | Correct Answer:

|
| Correct Answer | A |
Explanation Explanation/Reference: Explanation: Before a routing table is used, the destination cache is checked for an entry matching the destination address in the packet being forwarded. If the destination cache does not contain an entry for the destination address, the routing table is used to determine: The next-hop address - For a direct delivery (in which the destination is on a local link), the next- hop address is the destination address in the packet. For an indirect delivery (in which the destination is not on a local link), the next-hop address is the address of a router. The next-hop interface - The interface identifies the physical or logical interface that is used to forward the packet either to its destination or to the next router. Reference: http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/dd379520%28v=WS.10%29.aspx
| Question ID 9976 | HOTSPOT
You have a DNS server named Server 1. Server1 runs Windows Server 2012 R2.The network ID is 10.1.1.0/24.
An administrator creates several reverse lookup zones.
You need to identify which reverse lookup zone is configured correctly.
Which zone should you identify?
To answer, select the appropriate zone in the answer area.
Hot Area:
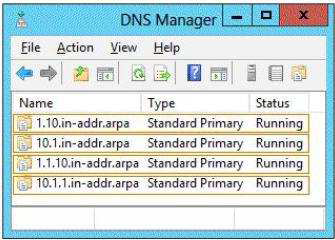
|
| Option A | Correct Answer:
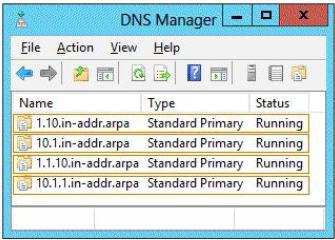
|
| Correct Answer | A |
Explanation Explanation/Reference: Explanation: Octets specified in reverse order
. . . . in-addr .arpa Reference: http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc961414.aspx