READ Free Dumps For Cisco- 400-101
| Question ID 18531 | What is Nagle's algorithm used for?
|
| Option A | To increase the latency
|
| Option B | To calculate the best path in distance vector routing protocols
|
| Option C | To calculate the best path in link state routing protocols
|
| Option D | To resolve issues caused by poorly implemented TCP flow control.
|
| Correct Answer | D |
Explanation Explanation: Silly window syndrome is a problem in computer networking caused by poorly implemented TCP flow control. A serious problem can arise in the sliding window operation when the sending application program creates data slowly, the receiving application program consumes data slowly, or both. If a server with this problem is unable to process all incoming data, it requests that its clients reduce the amount of data they send at a time (the window setting on a TCP packet). If the server continues to be unable to process all incoming data, the window becomes smaller and smaller, sometimes to the point that the data transmitted is smaller than the packet header, making data transmission extremely inefficient. The name of this problem is due to the window size shrinking to a "silly" value. When there is no synchronization between the sender and receiver regarding capacity of the flow of data or the size of the packet, the window syndrome problem is created. When the silly window syndrome is created by the sender, Nagle's algorithm is used. Nagle's solution requires that the sender sends the first segment even if it is a small one, then that it waits until an ACK is received or a maximum sized segment (MSS) is accumulated. Reference: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Silly_window_syndrome
| Question ID 18532 | Refer to the exhibit.
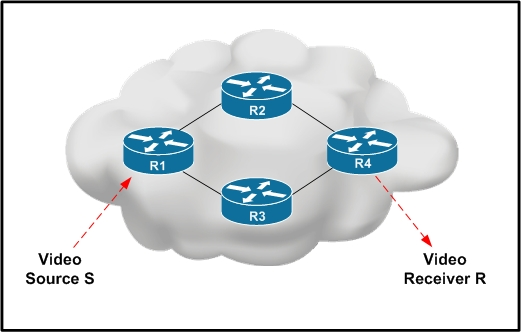
Video Source S is sending interactive video traffic to Video Receiver R. Router R1 has
multiple routing table entries for destination R. Which load-balancing mechanism on R1 can
cause out-of-order video traffic to be received by destination R?
|
| Option A | per-flow load balancing on R1 for destination R
|
| Option B | per-source-destination pair load balancing on R1 for destination R
|
| Option C | CEF load balancing on R1 for destination R
|
| Option D | per-packet load balancing on R1 for destination R
|
| Correct Answer | D |
Explanation Explanation: Per-packet load balancing guarantees equal load across all links, however potentially the packets may arrive out-of-order at the destination as differential delay may exist within the network. Reference: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/hw/modules/ps2033/prod_technical_reference09186 a00800afeb7.html
