READ Free Dumps For Cisco- 400-101
| Question ID 18515 | Refer to the exhibit.
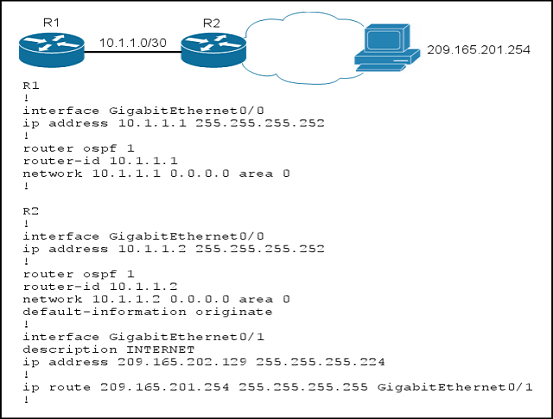
Routers R1 and R2 are configured as shown, and traffic from R1 fails to reach host
209.165.201.254.
Which action can you take to correct the problem?
|
| Option A | Ensure that R2 has a default route in its routing table.
|
| Option B | Change the OSPF area type on R1 and R2.
|
| Option C | Edit the router configurations so that address 209.165.201.254 is a routable address.
|
| Option D | Remove the default-information originate command from the OSPF configuration of R2.
|
| Correct Answer | A |
Explanation Explanation: Not sure that any of these answers are correct, it appears that this configuration is valid for reaching that one specific host IP. Answer A does have a route to that host so it would not need a default route to get to it. Choice B is incorrect as the area types have nothing to do with this. C is incorrect as that IP address is routable, and D is needed so that R1 will have a default route advertised to it from R2 so that it can reach this destination.
| Question ID 18516 | Which TCP mechanism prevents the sender from sending data too quickly for the receiver
to process?
|
| Option A | Congestion control
|
| Option B | Error detection
|
| Option C | Selective acknowledgement
|
| Option D | Flow control
|
| Correct Answer | D |
Explanation Explanation: In data communications, flow control is the process of managing the rate of data transmission between two nodes to prevent a fast sender from overwhelming a slow receiver. It provides a mechanism for the receiver to control the transmission speed, so that the receiving node is not overwhelmed with data from transmitting node. Reference: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Flow_control_(data)
