| Answer: Here are the solution as
below: Explanation:
First we have to figure out why R3 and R4 can not communicate with each other. Use the show
running-config command on router R3.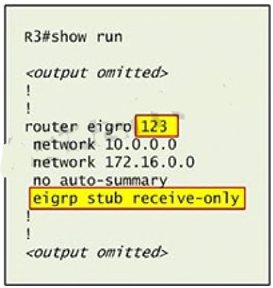
Notice that R3 is configured as a stub receive-only router. The receive-only keyword will restrict
the router from sharing any of its routes with any other router in that EIGRP autonomous system.
This keyword will also prevent any type of route from being sent. Therefore we will remove this
command and replace it with the eigrp stub command:
R3# configure terminal R3(config)# router eigrp 123 R3(config-router)# no eigrp stub receive-only
R3(config-router)# eigrp stub
R3(config-router)# end
Now R3 will send updates containing its connected and summary routes to other routers. Notice
that the eigrp stub command equals to the eigrp stub connected summary because the connected
and summary options are enabled by default.
Next we will configure router R3 so that it has only 2 subnets of 10.0.0.0 network. Use the show ip
route command on R3 to view its routing table:
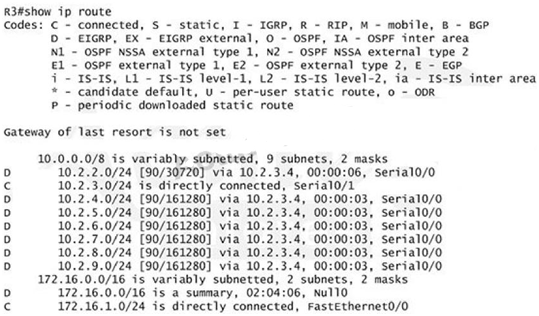
Because we want the routing table of R3 only have 2 subnets so we have to summary subnetworks
at the interface which is connected with R3, the s0/0 interface of R4.
There is one interesting thing about the output of the show ip route shown above: the 10.2.3.0/24,
which is a directly connected network of R3. We can’t get rid of it in the routing table no matter
what technique we use to summary the networks. Therefore, to make the routing table of R3 has
only 2 subnets we have to summary other subnets into one subnet.
In the output if we don’t see the summary line (like 10.0.0.0/8 is a summary...) then we should use
the command ip summary-address eigrp 123 10.2.0.0 255.255.0.0 so that all the ping can work
well.
In conclusion, we will use the ip summary-address eigrp 123 10.2.0.0 255.255.0.0 at the interface
s0/0 of R4 to summary.
R4> enable R4# conf t R4(config)# interface s0/0 R4(config-if)# ip summary-address eigrp 123 10.2.0.0 255.255.0.0
Now we jump back to R3 and use the show ip route command to verify the effect, the output is
shown below:
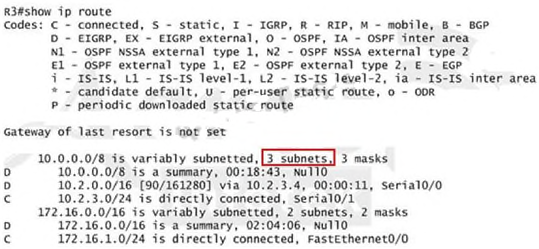
Note: Please notice that the IP addresses and the subnet masks in your real exam might be
different so you might use different ones to solve this question.
Just for your information, notice that if you use another network than 10.0.0.0/8 to summary, for
example, if you use the command ip summary-address eigrp 123 10.2.0.0 255.255.0.0 you will
leave a /16 network in the output of the show ip route command.
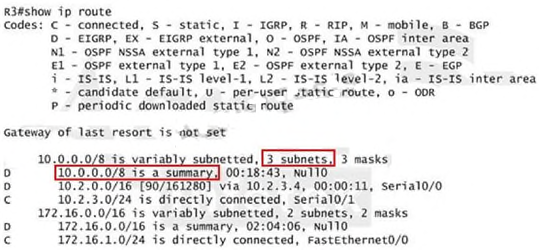
But in your real exam, if you don’t see the line "10.0.0.0/8 is a summary, Null0" then you can
summarize using the network 10.2.0.0/16. This summarization is better because all the pings can
work well.
Finally don’t forget to use the copy run start command on routers R3 and R4 to save the
configurations. R3(config-if)# end
R3# copy run start R4(config-if)# end
R4# copy run start
If the “copy run start” command doesn’t work then use “write memory.”
| 










